How to configure Context Write capability?
1. Introduction
The Context Write functionality in TrendMiner allows context items (events) created within TrendMiner to be pushed to Shiftconnector. This capability ensures alignment between TrendMiner and external platform by enabling real-time synchronization of event data.
By using context write, organizations can streamline communication between systems, reduce duplication of manual entry, and ensure a single source of truth across platforms.
2. Prerequisites
To use the Context Write functionality, ensure the following:
The data source must have write capability enabled and have writable types configured in ConfigHub (see below 3. Configure Write capability in ConfigHub)
The target system (Shiftconnector) must be correctly integrated and reachable
Licensing and feature toggle for context write may need to be enabled depending on your TrendMiner setup (please contact your CSM)
3. Configure Write capability in ConfigHub
3.1. Enable Write capability
Navigate to the ConfigHub/Data Sources page
Select an existing data source of type Shiftconnector or create a new one
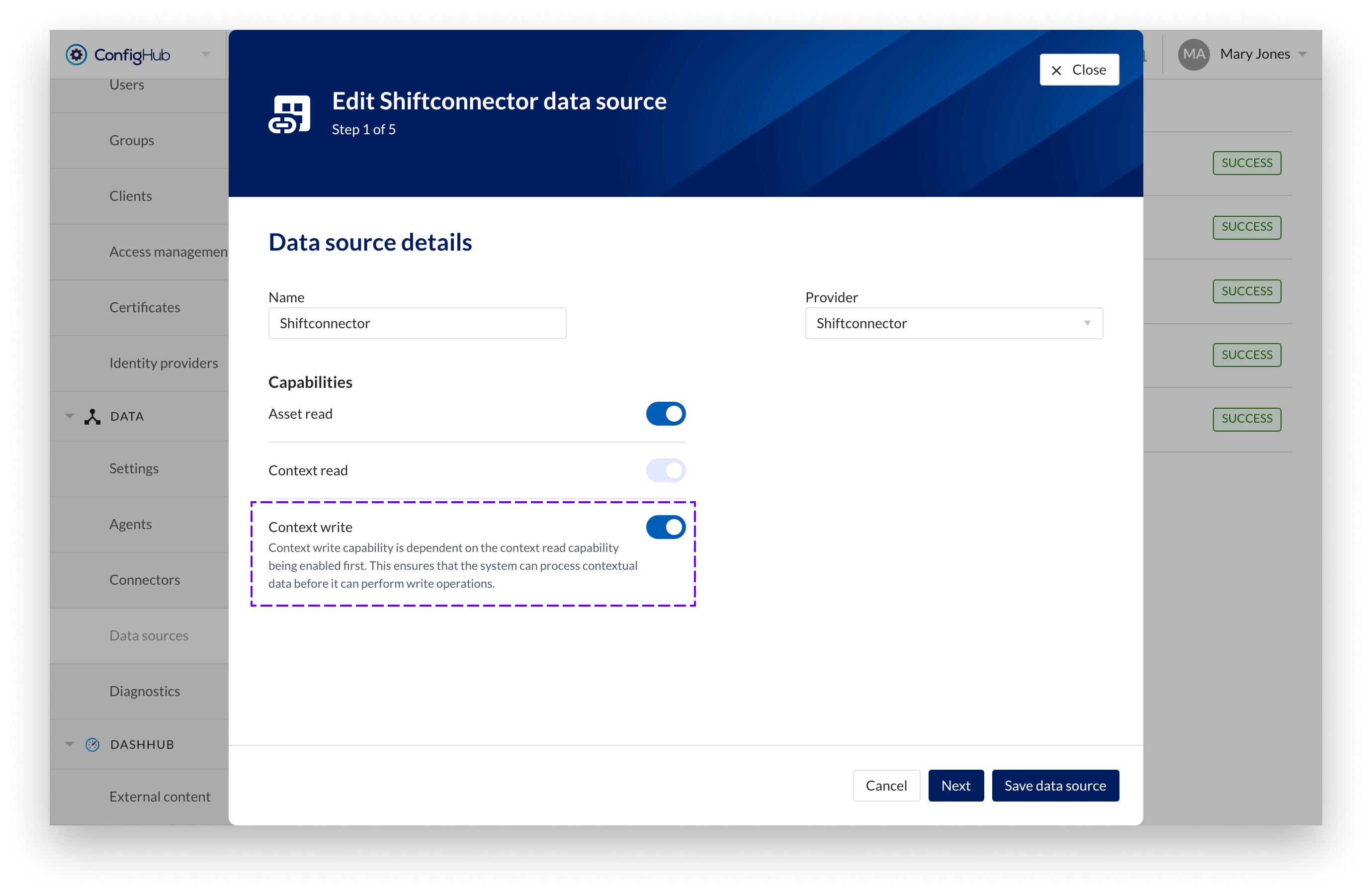
On Data source details step toggle Context write. This enables Context write capability for this datasource.
Note
Context write capability is dependent on the context read capability being enabled first. This ensures that the system can efficiently handle and process contextual information before it can perform write operations.
3.2. Assign writable types
On Context write details step enable Context Write feature
Enabling the write option will start pushing context items to the external system from the moment it is turned on. If you disable it, the data pushing is paused but context items will continue to be stored locally in TrendMiner and will be sent once write is re-enabled.
Note
This mechanism is particularly useful in situations where the external system is unavailable, undergoing maintenance, or experiencing performance issues for a certain period of time. By pausing the write operation, you avoid overloading or “hammering” the external service with requests, while still preserving all data for future delivery.
Specify deep link field (optional)
To enable seamless root cause analysis from Shiftconnector to TrendMiner, a deep link can be included in the payload during event write-back. This link opens the Context Item details panel in TrendMiner, providing immediate access to relevant event data.
To support deep linking, you must specify the Shiftconnector system name of the field where the deep link to the TrendMiner Context Item will be pushed to. This field must be configured for all types (referred to as categories in Shiftconnector) targeted for write-back.
Note
Note: The configuration of this field must be performed within Shiftconnector and may require assistance from your system administrator. For more information, please consult Shiftconnector documentation.
Assign writable types
In the left column you can see all active Shiftconnector categories that are mapped to TrendMiner types. Move the types to the right column to assign them as writable.
If a type is defined as writable, any events of that type will always be pushed to the external source. Ensure that you carefully select the types you designate as writable to avoid unintended data transfers.
Events of writable types will be excluded during the synchronization of events from the external system, as they originate from TrendMiner.
Tip
To maintain clear data flow, we recommend creating dedicated categories in Shiftconnector that are specifically intended for write-back from TrendMiner. This helps distinguish between externally pushed events and manually created ones, improving maintainability and traceability.

4. How to trigger Context Write
Context write can be triggered in two ways - automatically through monitors or manually by users. Only users with appropriate permissions to access the Shiftconnector asset structure will be able to use this functionality.
4.1. Automatically via monitors
Monitors in TrendMiner can be configured to automatically create context items based on defined conditions (e.g., specific process behavior or threshold breaches). If the context write feature is enabled and properly configured, these automatically created context items will also be pushed to Shiftconnector.
To set it up:
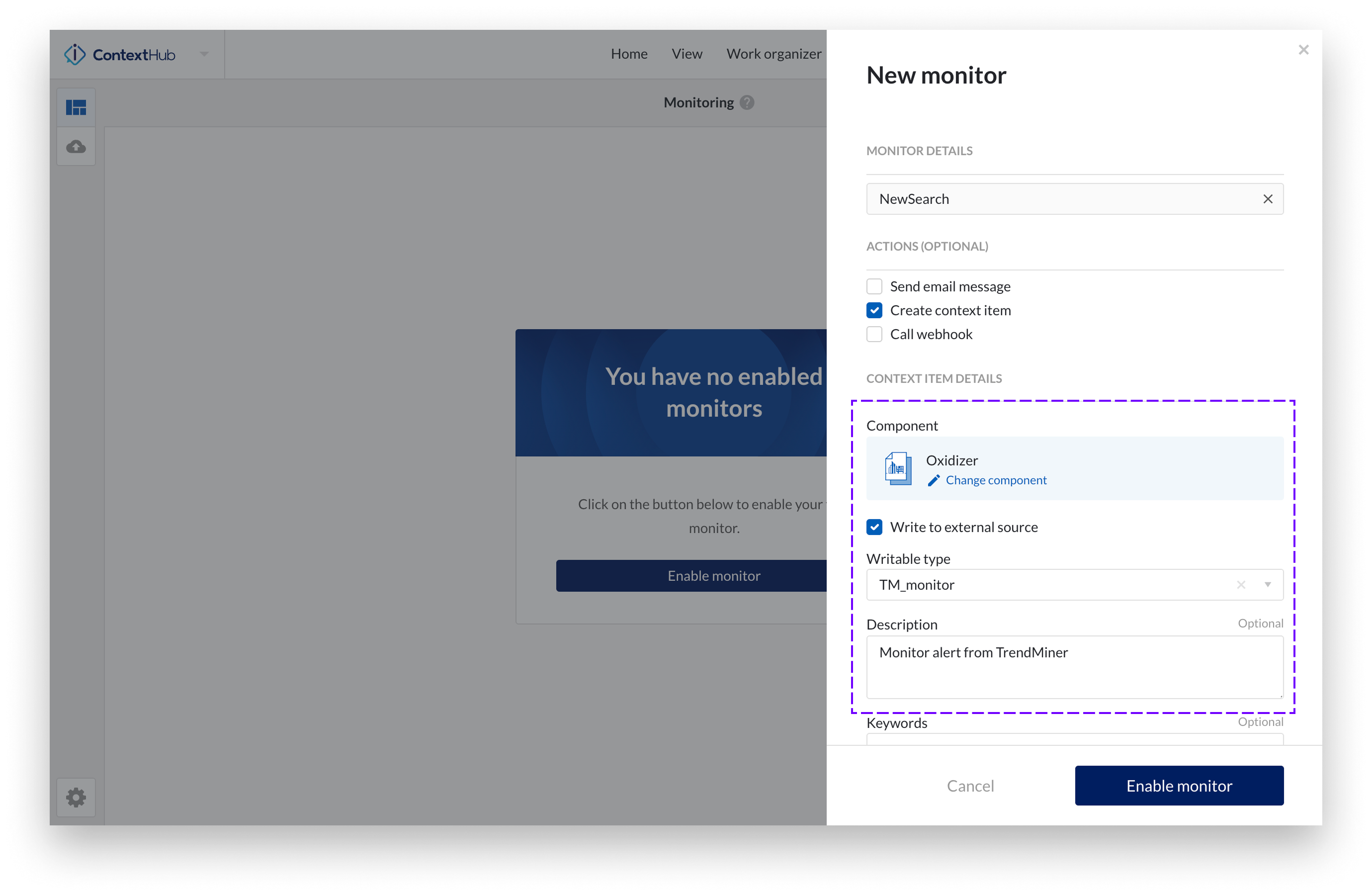
Select the correct component: The component must match the functional location in Shiftconnector where you want the context item to be created. This ensures correct mapping in the external system.
Enable 'Write to external source': When checked, a list of writable types will be displayed. These are the only types eligible to be pushed to external system.
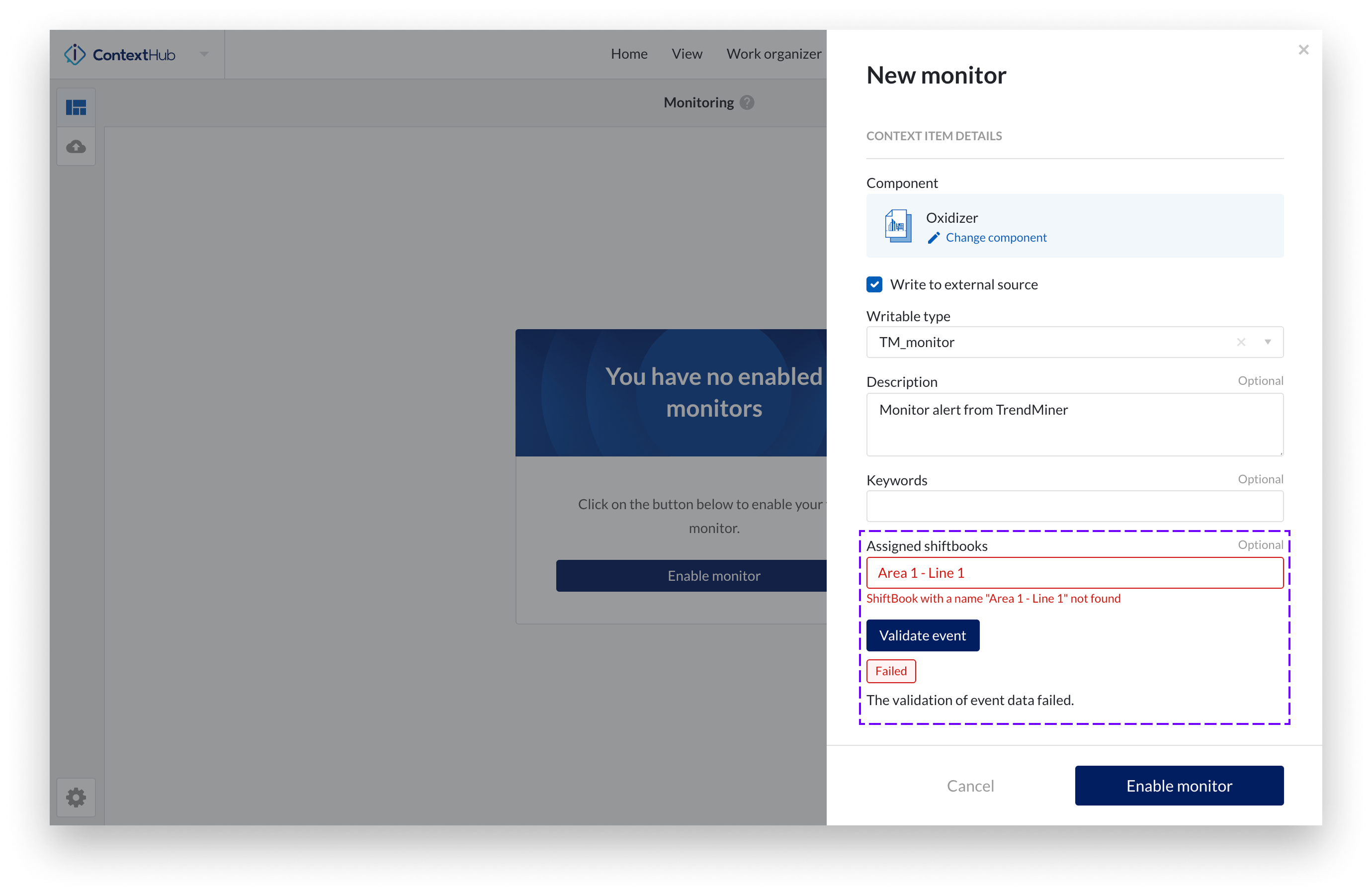
Fill in 'Assigned Shiftbooks' field: Enter the name(s) of the shiftbook(s) you want to assign to the context item. You can input multiple shiftbook names, separated by commas. Shiftbook names must match exactly with the names defined in Shiftconnector.
Note
Make sure that all mandatory fields are properly filled. Missing or misconfigured fields may result in write failures. A "Validate event" button is available to help confirm whether all required fields are present and correctly configured before the monitor starts creating events.
4.2. Manually via Context Item creation
Users can also manually create context items in TrendMiner. If the 'Write to external source' option is selected, the event will be pushed to Shiftconnector after creation — provided all required fields are filled in correctly.
Example of a Context Item in TrendMiner and its corresponding event in Shiftconnector:
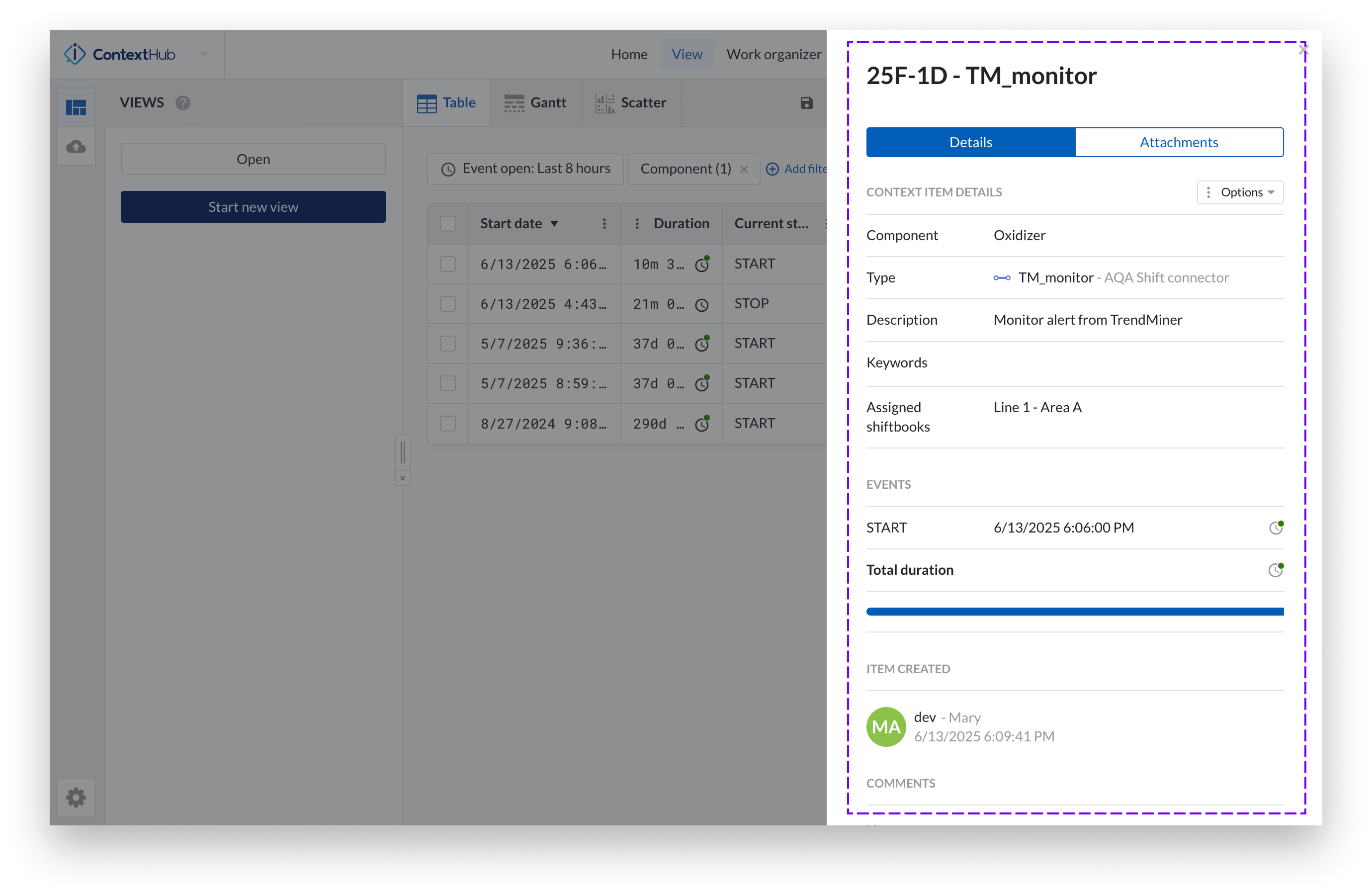
Context Item in TrendMiner
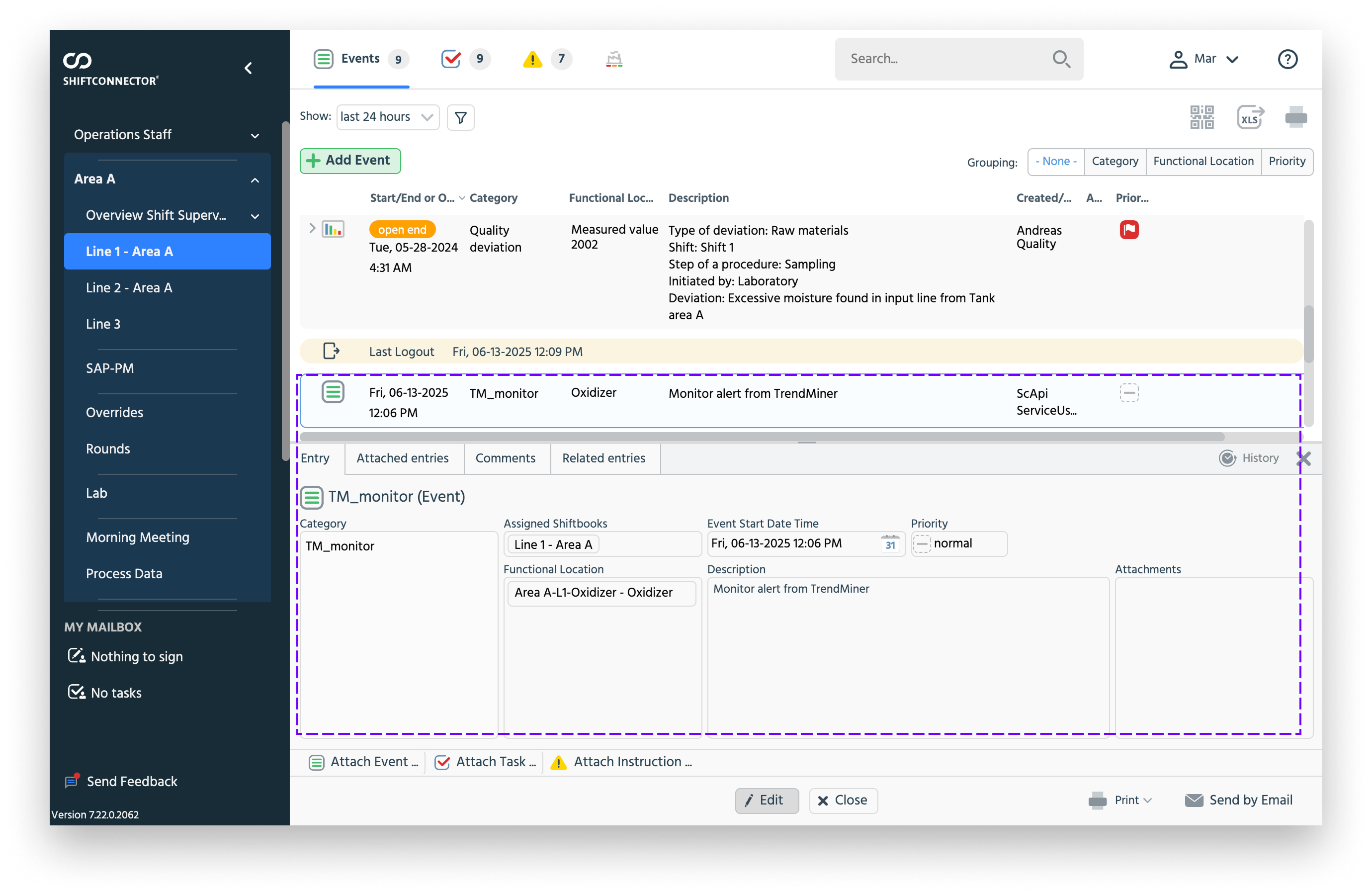
Event in Shiftconnector
5. Error handling and diagnostics
When a write operation to an external system fails—either due to repeated retry failures or an immediate client-side exception—TrendMiner will:
Offload the failed event to the Not Delivered Context Items table for inspection.
Automatically disable the write functionality for the affected data source to prevent further failed attempts.
Notify admin users via an in-app notification and email, prompting investigation and corrective action.
Note
To improve reliability, context item delivery supports retry attempts for up to 8 hours when an endpoint is temporarily unavailable. If all retries fail, the event is marked as failed, and the write toggle is disabled for that data source. At that point, manual intervention is required — either retry the failed write or purge it.
How retry mechanism works
The system retries failed event deliveries using an exponential backoff strategy.
This prevents overwhelming third party endpoint while ensuring retries continue for a reasonable duration.
Retry parameters
Setting | Value |
|---|---|
| Initial Delay | 1 minute (60 seconds) |
| Maximum Delay | 15 minutes (900 seconds) |
| Maximum Retry Period | 8 hours (28,800 seconds) |
What this means
The first retry happens 1 minute after the initial failure.
Each subsequent retry delay grows exponentially (multiplied by the backoff factor), capped at 15 minutes.
Retries stop after 8 hours from the first failure.
Admins can review and manage failed events via: ConfigHub → Diagnostics → Context Write
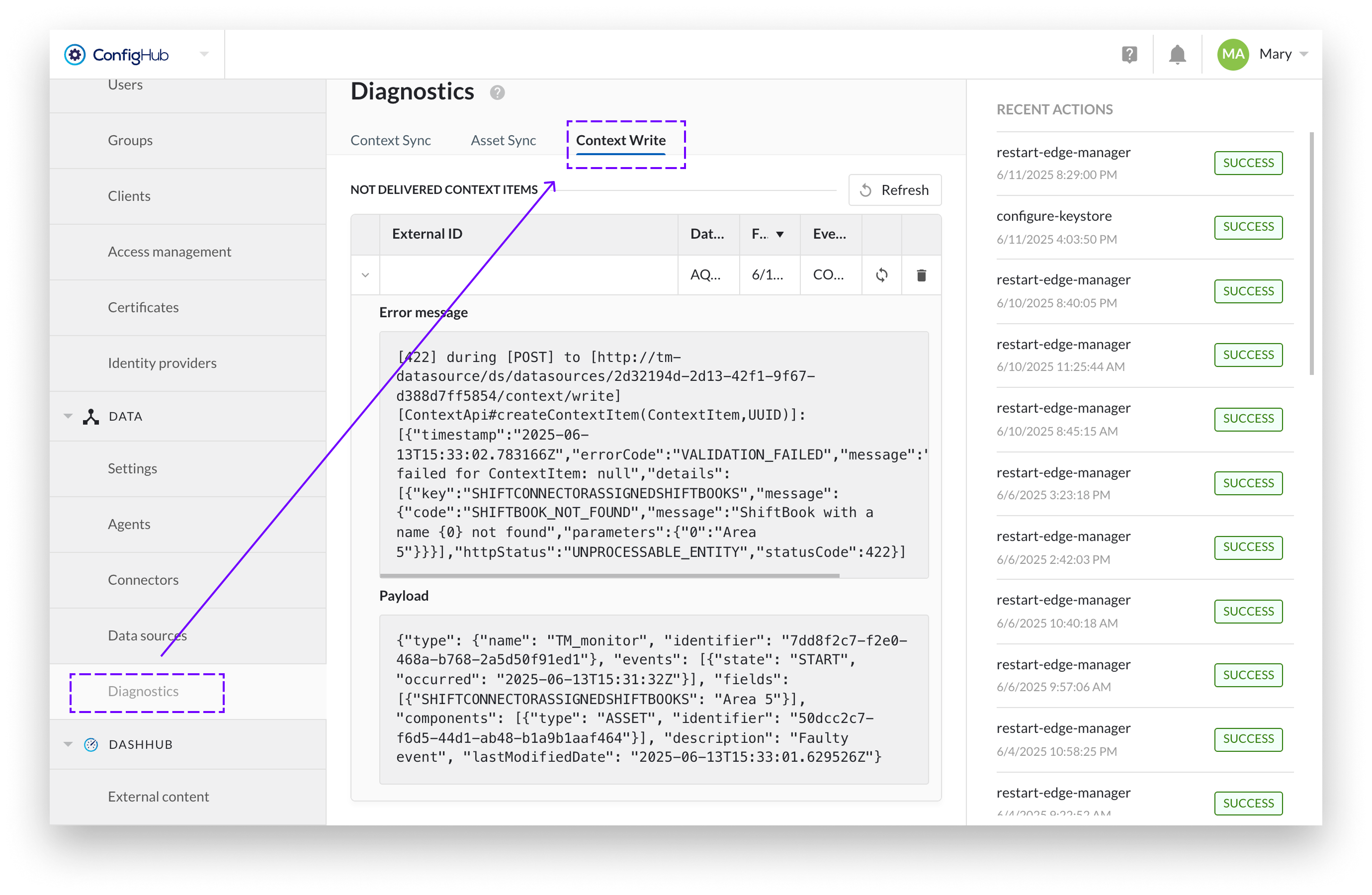
Available actions:
Retry: Attempt to resend the event after correcting any issues (e.g., system availability).
Purge: Permanently remove the failed event (and all erroneous records) from the processing queue (e.g., if the issue cannot be corrected, because the of misonfigured fields).
Typical failure reasons include:
Incorrectly configured events (e.g., missing required fields or invalid values)
Unreachable or unavailable external system (e.g., due to downtime or network issues)
Authentication or connection errors
Additionally, in the Write Settings administrators can define the number of parallel processing workers. This setting controls how many events can be processed simultaneously, allowing optimization based on system capacity and external system performance.
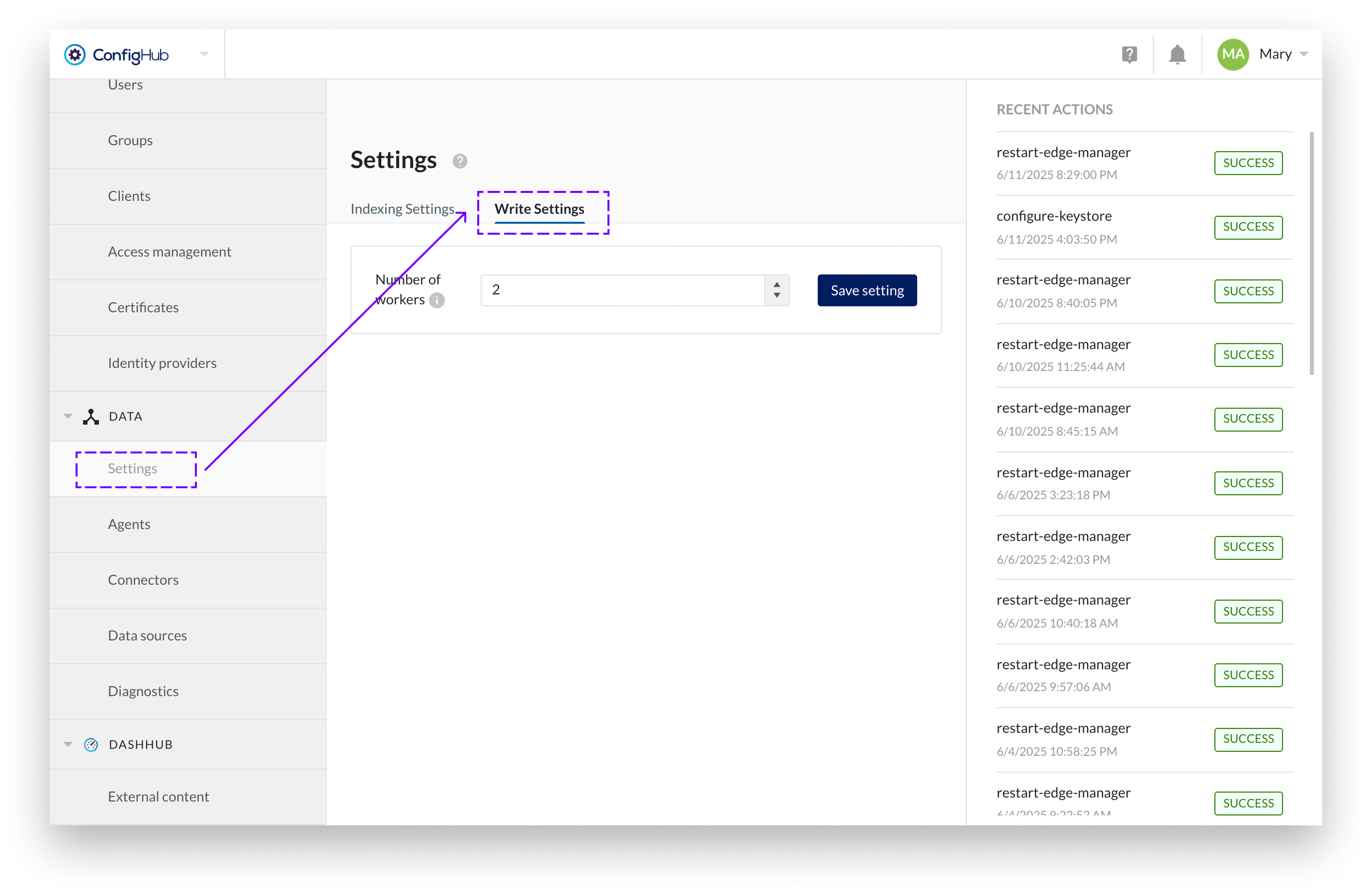
This mechanism ensures resilience, transparency, and controlled recovery from integration issues.